Monitoring radar altimetry at Issyk Kul in Kyrgyzstan | Issyk Kul Observatory
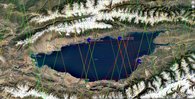



Satellites provide key observations of global sea level changes, but these measurements require continuous ground-based monitoring to ensure their quality and long-term stability. Since 2016, the GFZ has been building an observatory on Lake Issyk Kul together with CAIAG in Kyrgyzstan. This observatory can be used to carry out such controls remotely all year round. The observatory is situated on Lake Issyk Kul, the second largest mountain lake in the world, located 1600 meters above sea level with a year-round ice-free surface. With an area of approximately 180x70km, it is passed by all active and historical altimeter missions.
The first phase of the project involved installing a ROMPS station on the south bank of the lake and radar gauges on the north and south banks. The ROMPS station provides environmental parameters, such as wind and air pressure, which are used to correct the altimeter measurements. The GNSS station, also present, plays a dual role: it determines the geocentric height of the gauge measurements, ensuring comparability with satellite measurements, and calculates the tropospheric attenuation corrections, which can be compared with those of the satellite's radar signals.
The gauge measurements allow the water level of Issyk Kul to be continuously monitored and thus serve as a reference for lake level changes. In the following years, three more gauges were installed so that the water level across the entire lake can be measured.
Since 2017, we have been taking regular measurements using GNSS and radar sensors from a ship. Each of these ships passes directly under the nominal overflight path of the satellites. We combine these measurement profiles with tide gauge data. This allows us to check the satellite measurements against the ground measurements for each satellite overflight. We use various algorithms (OCEAN, MLE3, ICE1) to analyze the satellites, and our method allows us to analyze each of these independently.
Das Issyk Kul Observatory is part of the Global Change Observatory Central Asia (GCOCA).
Project partners:
- Central Asian Institute for Applied Geosciences (CAIAG)
Project duration:
- 2016 -
Budget:
Household, ACROSS initiative und GCOCA Observatory
Project-related publications:
- Schöne, T. et al. (2024). Performance Analyses of Sentinel-3A and Sentinel-3B Over Lake Issyk Kul (Kyrgyzstan). In: International Association of Geodesy Symposia. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. doi.org/10.1007/1345_2024_268
- Zech, C., Schöne, T., Illigner, J., Stolarczuk, N., Queißer, T., Köppl, M., Thoss, H., Zubovich, A., Sharshebaev, A., Zakhidov, K., Toshpulatov, K., Tillayev, Y., Olimov, S., Paiman, Z., Unger-Shayesteh, K., Gafurov, A., & Moldobekov, B. (2021). Hydrometeorological data from a Remotely Operated Multi-Parameter Station network in Central Asia. Earth System Science Data, 13(3), 1289-1306. doi:10.5194/essd-13-1289-2021
- (Data publication) Zech, C., Schöne, T., Illigner, J., Stolarczuk, N., Queißer, T., Köppl, M., Thoss, H., Zubovich, A., Sharshebaev, A., Zakhidov, K., Toshpulatov, K., Tillayev, Y., Olimov, S., Paiman, Z., Unger-Shayesteh, K., Gafurov, A., Moldobekov, B. (2020): Hydrometeorological data from ROMPS network in Central Asia. doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.1.2.2020.002


