Geological Storage

Background
Due to the increasing importance of renewable energies and the need to reduce CO₂ emissions, the storage of CO₂ and hydrogen underground is a key technology for a climate-neutral future.
Direct Air Capture and Storage (DACS) technology allows CO2 to be extracted from the air and permanently stored in geological formations. The gas can also be used as a working fluid in a geothermal plant, which opens up the possibility of contributing to a climate-neutral energy transition.
To reduce further CO₂ emissions, the decarbonisation of all sectors and the expansion of renewable energies is necessary. Using hydrogen storage enables surplus energy from renewable sources to be stored and fluctuations in energy production to be balanced out. Hydrogen is also a raw material for industry and can be used for cross-sector electricity and heat generation.
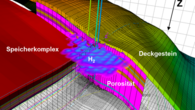
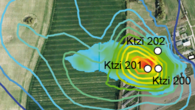
Research of the regional geology is essential for successful underground storage. From geological models and numerical simulations to practical laboratory tests and on-site investigations, we are working on understanding gas dispersion and its effects on the surrounding rock to develop efficient storage technologies.
Key Scientific Questions
- How can a CO₂-based geothermal cycle with integrated CO₂ -storage be technically and economically optimized?
- How can Direct Air Capture and Storage (DACS) technology be improved and scaled to achieve sustainable CO₂ neutrality?
- Can a saline aquifer serve as an efficient and economically viable porous storage for hydrogen?
Related Projects


